Node.js is known for its ability to handle high-performance, non-blocking I/O operations, making it a popular choice for building scalable applications. At the heart of this efficiency lies the event loop—a core mechanism that manages asynchronous operations in Node.js.
In this blog, we’ll explore:
- What the event loop is
- How it works
- Different phases of the event loop
- How it impacts performance
- Common pitfalls and best practices
1. What is the Event Loop in Node.js?
The event loop is a mechanism that allows Node.js to perform non-blocking I/O operations—even though JavaScript runs on a single thread—by offloading operations to the system kernel whenever possible.
In simple terms:
- Node.js is single-threaded for JavaScript execution.
- The event loop ensures asynchronous tasks like file reads, network requests, and timers don’t block code execution.
Think of it as a traffic controller that decides when and how to execute your code, callbacks, and other operations.
2. Why Do We Need the Event Loop?
Without the event loop:
- Each task would have to complete before the next starts.
- Long-running operations (like file reading or API calls) would freeze the application.
With the event loop:
- Long-running tasks are handled asynchronously.
- The main thread remains free to handle new incoming requests.
This makes Node.js fast and efficient for I/O-heavy operations.
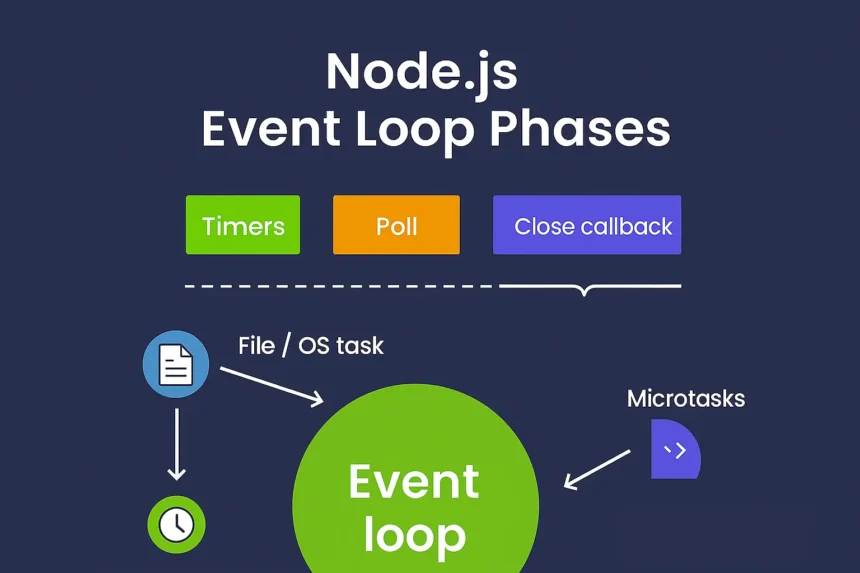
3. How the Event Loop Works
The event loop constantly checks if there’s work to be done. If there is, it processes tasks in specific phases.
Phases of the Event Loop:
- Timers Phase
- Executes callbacks from
setTimeout()andsetInterval(). - Example: jsCopyEdit
setTimeout(() => console.log('Timer callback'), 1000);
- Executes callbacks from
- Pending Callbacks Phase
- Executes I/O callbacks that were deferred.
- Idle, Prepare Phase(internal use)
- Used internally by Node.js, usually not directly accessed by developers.
- Poll Phase
- Retrieves new I/O events; executes I/O-related callbacks.
- If no timers are pending, the poll phase can wait for new events.
- Check Phase
- Executes
setImmediate()callbacks. - Example: jsCopyEdit
setImmediate(() => console.log('Immediate callback'));
- Executes
- Close Callbacks Phase
- Executes callbacks for closed connections like sockets.
4. Event Loop Example
jsCopyEditconsole.log('Start');
setTimeout(() => console.log('Timeout callback'), 0);
setImmediate(() => console.log('Immediate callback'));
console.log('End');
Possible Output:
pgsqlCopyEditStart
End
Timeout callback
Immediate callback
(Order between timeout and immediate may vary depending on execution timing.)
5. Event Loop and Asynchronous Operations
The event loop works with:
- Timers (
setTimeout,setInterval) - I/O callbacks (file system, network)
- Promises and async/await (microtasks)
Important: Promises and process.nextTick() are part of the microtask queue, which is executed immediately after the current phase finishes, before moving to the next phase.
Example:
jsCopyEditconsole.log('A');
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log('B'));
process.nextTick(() => console.log('C'));
console.log('D');
Output:
cssCopyEditA
D
C
B
6. Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Blocking the Event Loop
- CPU-heavy operations (like large loops) can block the loop and freeze the app.
- Overusing
process.nextTick()- Can cause infinite loops if not used carefully.
- Mixing timers and immediate callbacks without understanding order
7. Best Practices
✅ Use asynchronous methods for I/O operations.
✅ Offload CPU-intensive tasks to worker threads or child processes.
✅ Monitor event loop lag for performance issues using tools like libuv or clinic.
✅ Understand microtask vs macrotask queues to avoid unexpected behavior.
8. Final Thoughts
The event loop is the backbone of Node.js’s asynchronous nature. Mastering it helps you:
- Write non-blocking code
- Optimize performance
- Avoid unexpected behavior in your applications
By understanding how different phases work and how Node.js schedules tasks, you can build faster, more efficient applications.